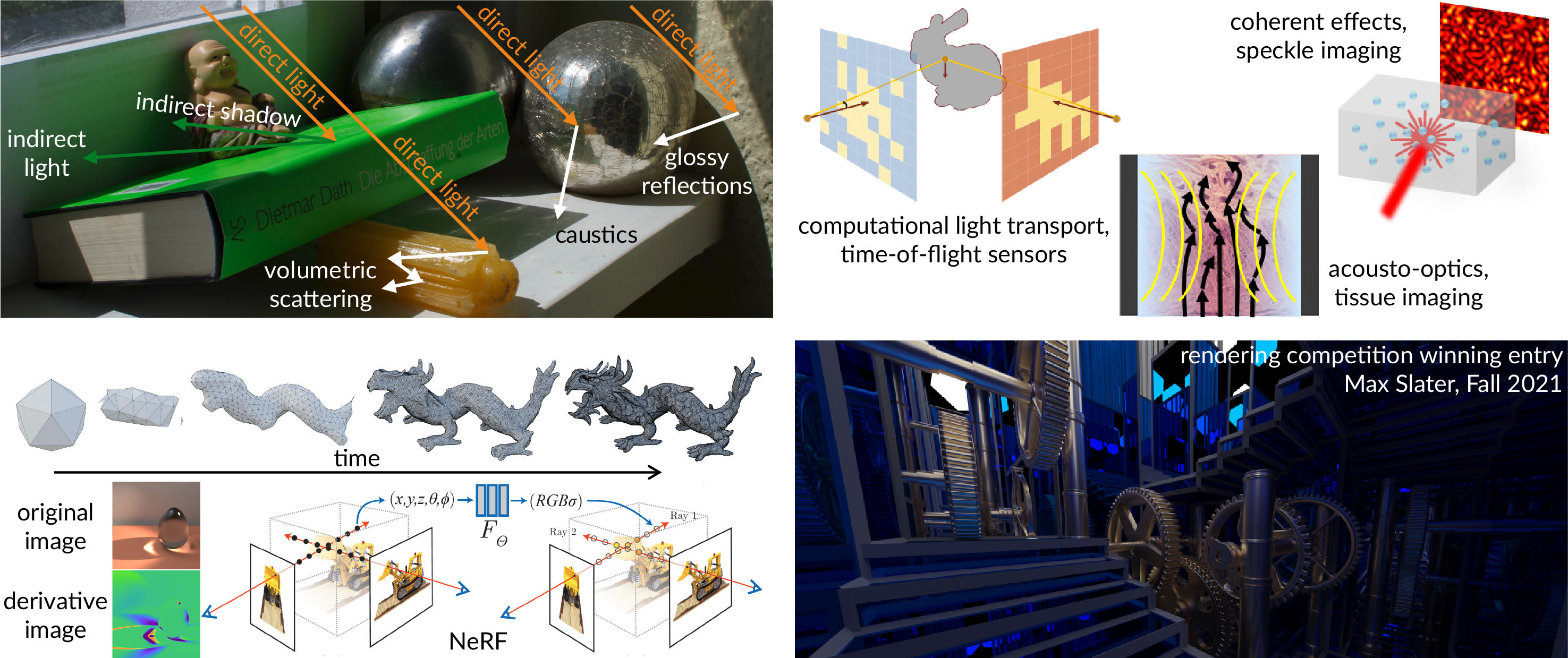
Course description
This course is an introduction to physics-based rendering at the advanced undergraduate and introductory graduate level. During the course, we will cover fundamentals of light transport, including topics such as the rendering and radiative transfer equations, light transport operators, path integral formulations, and approximations such as diffusion and single scattering. Additionally, we will discuss state-of-the-art models for illumination, surface and volumetric scattering, and sensors. Finally, we will use these theoretical foundations to develop Monte Carlo algorithms and sampling techniques for efficiently simulating physically-accurate images. Towards the end of the course, we will look at advanced topics such as rendering wave optics, neural rendering, and differentiable rendering.
The course has a strong programming component, in the form of assignments through which students will develop their own working implementation of a physics-based renderer, including support for a variety of rendering algorithms, materials, illumination sources, and sensors. The course also emphasizes theoretical aspects of physics-based rendering, through weekly take-home quizzes. Lastly, the course includes a final project, during which students will select and implement some advanced rendering technique, and use their implementation to produce an image that is both technically and artistically compelling. The course will conclude with a rendering competition, where students submit their rendered images to win prizes.
Cross-listing: This is both an advanced undergraduate and introductory graduate course, and it is cross-listed as 15-468 (for undergraduate students), 15-668 (for Master's students), and 15-868 (for PhD students). Please make sure to register for the section of the class that matches your current enrollment status.
Competitions
Programming assignment competitions: The submissions and results for the programming assignment competitions are available in the following pages.
Rendering competition: The submissions and results are available in the rendering competition page. You can also browse all final project presentations.
Prerequisites
This course requires familiarity with linear algebra, calculus, programming, data structures, algorithms, and doing computations with images. In particular, either of the following courses can serve as proof that you satisfy these prerequisites:
- 16-385 Computer Vision, OR
- 16-720 Computer Vision, OR
- 16-820 Advanced Computer Vision, OR
- 15-462/15-662 Computer Graphics, OR
- 15-463/15-663/15-862 Computational Photography.
If you want to enroll but have not taken any of the above courses, please make sure to contact the instructor! We make a lot of exceptions each year, on a case-by-case basis.
Textbooks
Readings will be assigned primarily from the following textbooks, which can also be useful references in general. All of them are available online from the CMU library:
- Physically Based Rendering: From Theory To Implementation, by Matt Pharr, Wenzel Jakob, and Greg Humphreys.
- Robust Monte Carlo Methods for Light Transport Simulation, by Eric Veach.
- Physically Based Rendering: From Theory To Implementation, by Matt Pharr, Wenzel Jakob, and Greg Humphreys.
- Advanced Global Illumination, by Philip Dutre, Philippe Bekaert, Kavita Bala.
- Monte Carlo Theory, Methods, and Examples, by Art Owen.
Evaluation
The final grade will comprise:
- Four two-week programming assignments (50%).
- Ten take-home quizzes (20%).
- Final project and rendering competition (25%).
- Class participation (5%).
Programming assignments: The series of programming assignments (PAs) involves starting from a very basic ray tracing framework, and using it to implement increasingly more sophisticated rendering capabilities. Programming will be in C++.
Take-home quizzes: Take-home quizzes (TQs) will each require solving two-three theory questions related to the corresponding week's two lectures. Answers will need to be typed in LaTeX, and we encourage students to use the Overleaf 15-468 take-home quiz solution template.
Final project and rendering competition: Towards the end of the semester, each student will work on a project of their own choosing. The purpose of the project is to enhance the renderer from PAs with advanced features, and use it to generate images that are both physically accurate and artistically compelling. Each student will submit an image they produce for consideration in an end-of-semester competition, judged by other faculty and graduate students at CMU. Submissions will be selected for a technical award and an art award, and the two winning students will receive fully-funded trips (registration, travel, lodging) to SIGGRAPH 2023. Students will also receive a separate grade, independently of the results of the competition. Final project presentations will be scheduled during the final exam period. Details are available in the final project page.
Programming assignment competitions: For each progamming assignment, the teaching staff will select the student that produced the best result when designing and rendering their own scenes. The winning student will receive a gift card. The competition is separate from the grade for each programming assignment.
Submitting homework and deadlines: We will use Canvas for submitting and grading homeworks.
Late days: For the programming assignments, students will be allowed a total of five free late days. Any additional late days will each incur a 10% penalty. Additionally, no programming assignment may be submitted more than three days after its due date. Please note that submission deadlines will be enforced strictly for the purposes of counting late days. In particular, no exceptions will be made for reasons such as upload delays, submitting incorrect files, and so on.
Missed quizzes: For the take-home quizzes, students will be allowed to skip a total of two quizzes without penalty. Students may submit more than eight quizzes for extra credit, e.g., submitting perfect solutions to ten quizzes will contribute to the final grade as 20% standard and 5% extra credit. There are no free late days for quizzes, and any late quiz will receive zero credit.
Collaboration policy: We encourage students to work in groups, but each student must submit their own work. This includes: writing their own code, rendering their own scenes, coming up with their own math solutions, and producing their own writeup. If students work as a group, they must include the names of their collaborators in their writeup. Students absolutely must not share or copy code, data, or text from any source. Additionally, students must not use any external code or data unless explicitly permitted. These and any other forms of cheating are prohibited and will result in a failing grade for the entire course (not just the assignment they are caught on). If you are uncertain about whether some activity would be cheating, just be cautious and ask the teaching staff before proceeding. Additionally, students must not supply any code or writeups they complete during this course to other students in future instances of the course, or make this material available (e.g., on the web) for use in future instances of the course. Students must make sure any online repositories they use for the course are kept private.
15-668, 15-868: Students taking 15-668 or 15-868 will complete a more substantial final project, and submit a longer paper describing their project.
Meetings
Lectures: Lectures will take place in Wean Hall 5409. All lectures will be recorded, and recordings will be available on Canvas after each lecture.
Recitations: The course includes optional weekly recitations on Wednesdays, 3:00 - 5:00 pm ET, taking place in Smith Hall (EDSH) 236 (graphics lounge). During the recitations, we will go over solutions to the take-home quizzes.
Reading group: In addition to regular lectures, the course includes an optional reading group taking place every second Friday, 2:30 - 4:00 pm ET in Smith Hall (EDSH) 236 (graphics lounge). During the reading group, we will go over recent papers and advanced topics selected by the students and instructors.
Email, office hours, and discussion
Email: Please use [15468] in the title when emailing the teaching staff!
Office hours: Teaching staff will have regular office hours at the following times:
- Mondays 3:00 - 5:00 pm ET, Yannis.
- Tuesdays 3:00 - 5:00 pm ET, Hanyu.
- Thursdays 4:00 - 6:00 pm ET, Jeff.
All office hours will take place in person in Smith Hall (EDSH) 236 (graphics lounge).
Feel free to email us about scheduling additional office hours. Please do not email the teaching staff with questions about homework or grading. You should post those on Piazza or Slack.
Discussion: We will use Piazza and Slack for course discussion and announcements. Instructions for accessing the course Slack server are available on Piazza.
Interested in research?
We are actively looking for students at all levels (undergraduate, MS, PhD) to help in projects on various aspects of rendering, computational photography, imaging, and graphics in general. If you are interested, please send Yannis an email (or talk to him in person in class).
You should also take a look at the Carnegie Mellon Computational Imaging website and YouTube channel, as well as the Carnegie Mellon Graphics website, to find more information about related projects active here at CMU.
Finally, you are welcome to attend the weekly graphics lab meetings during the semester. If you want to receive announcements about the meetings, as well as other emails regarding rendering and graphics, please ask Yannis to add you to the graphics lab's mailing list.
(Tentative) syllabus
Dates and topics are likely to change during the semester. Slides will be uploaded on this website before each lecture.
| Date | Topics | Homework |
|---|---|---|
| Tu, Jan 17 | Introduction | |
| Th, Jan 19 | Ray tracing and geometric representations | |
| Tu, Jan 24 | Ray tracing and simple shading | TQ1 out |
| Th, Jan 26 | Texture mapping | |
| Fr, Jan 27 | PA1 out | |
| Tu, Jan 31 | Procedural textures | TQ1 due, TQ2 out |
| Th, Feb 2 | Radiometry | |
| Fr, Feb 3 | Reading group: specular next-event estimation | |
| Tu, Feb 7 | Microfacet BRDFs | TQ2 due, TQ3 out |
| Th, Feb 9 | Monte Carlo integration | |
| Fr, Feb 10 | PA1 due, PA2 out | |
| Tu, Feb 14 | Quasi-Monte Carlo sampling | TQ3 due, TQ4 out |
| Th, Feb 16 | Direct illumination | |
| Fr, Feb 17 | Reading group: layered materials | |
| Tu, Feb 21 | Path tracing | TQ4 due, TQ5 out |
| Th, Feb 23 | Participating media | |
| Fr, Feb 24 | PA2 due, PA3 out | |
| Tu, Fen 28 | Path integral formulation | TQ5 due, TQ6 out |
| Th, Mar 2 | Bidirectional light transport | |
| Fr, Mar 3 | Reading group: ReSTIR | |
| Tu, Mar 7 | No class (Spring Break) | |
| Th, Mar 9 | No class (Spring Break) | |
| Tu, Mar 14 | Photon mapping | TQ6 due, TQ7 out |
| Th, Mar 16 | Markov chain Monte Carlo rendering | |
| Fr, Mar 17 | PA3 due, PA4 out | |
| Tu, Mar 21 | Inverse and differentiable rendering | TQ7 due, TQ8 out |
| Th, Mar 23 | Rendering for scientific imaging applications | |
| Fr, Mar 24 | Reading group: non-exponential transport | |
| Tu, Mar 28 | Neural rendering and wrap up | TQ8 due, TQ9 out |
| Th, Mar 30 | Advanced topics | |
| Fr, Mar 31 | PA4 due | |
| Tu, Apr 4 | Advanced topics | TQ9 due, TQ10 out |
| Th, Apr 6 | Advanced topics | |
| Fr, Apr 7 | Proposal due | |
| Tu, Apr 11 | Advanced topics | |
| Th, Apr 13 | No class (Spring Carnival) | |
| Tu, Apr 18 | Advanced topics | TQ10 due |
| Th, Apr 20 | Guest lecture | |
| Fr, Apr 21 | Reading group: operator-theoretic light transport | |
| Tu, Apr 25 | Guest lecture | |
| Th, Apr 27 | Wrap up | |
| Fr, Apr 28 | Reading group: frequency-space analysis of light transport |
Previous course offerings
- 15-468 (15-668, 15-868), Spring 2022 (taught by Ioannis Gkioulekas)
- 15-468 (15-668, 15-868), Spring 2021 (taught by Ioannis Gkioulekas)
Similar courses elsewhere
- Rendering Algorithms (Wojciech Jarosz, Dartmouth)
- Advanced Computer Graphics (Wenzel Jakob, EPFL)
- Image Synthesis Techniques (Pat Hanrahan and Matt Pharr, Stanford)
- Computer Graphics II: Rendering (Ravi Ramamoorthi, UCSD)
- Advanced Image Synthesis (Tzu-Mao Li, UCSD)
- Realistic Image Synthesis Steve Marschner, Cornell)
Acknowledgments
The materials for this course have been pieced together from many different people and places. The instructor is particularly indebted to Wojciech Jarosz and Wenzel Jakob, who generously provided the materials of their courses at Dartmouth and EPFL, respectively. These materials formed the basis for the first offering of this course. Special thanks to the following colleagues for sharing their course materials or making them available online (in alphabetical order): Steven Gortler, Pat Hanrahan, Steve Marschner, Srinivasa Narasimhan, Matt Pharr, Matthew O'Toole, Ravi Ramamoorthi, Todd Zickler. Individual slides and homework assignments include their own credits.